Module 1. What is Neo4j?
Course 4. Building Graphs in Neo4j
Estimated Time: 25–30 minutes
🧭 Module Objectives
- Explain what Neo4j is and what makes it different from other databases.
- Describe the basic concepts of nodes, relationships, and properties.
- Understand why graph databases are especially well-suited for the humanities.
- Identify the main Neo4j products (Aura, Desktop, Server) and know which one this course uses.
From Meaning to Data and—now—to Graphs
In our earlier courses, we explored:
- How the Wellespring Project models songs, people, and ideas as data (course 1 and course 2).
- What data is and how we use relationships to represent meaning and connection (course 2).
- How modeling turns interpretation into structure (course 3).
Now, we'll take the next step: actually building and exploring those relationships using a graph database called Neo4j. Think of this course as moving from "drawing a map" to "walking through the map."
Neo4j is the tool that lets us build, visualize, and query those networks of meaning: whether we're tracing Jesse Welles' creative collaborations, linking lyrics to emotions, or connecting songs to their social contexts.
We could do similar things for all sorts of humanities and social science topics: connecting characters, places, and events in J.R.R. Tolkien's Middle Earth; comparing scriptures from various world religions; tracking the key events, people, and issues of the US Civil War. The applications are endless, so even if Jesse Welles is not a topic you would choose, do proceed with wide practical applications in the back of your mind.
What is Neo4j?
Neo4j is a graph database: a system designed to store and query data that's connected in complex ways. Traditional databases (like spreadsheets or SQL tables) arrange information in rows and columns. Neo4j, instead, represents information as a network of nodes and relationships.
The Property Graph Model
Neo4j uses what's called the property graph model, made up of three main parts:
| Concept | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Node | Represents an entity or "thing." | A person, song, place, or idea. |
| Relationship | Connects two nodes, showing how they're related. |
A Person WROTE a Song. |
| Property | Stores information about a node or relationship. |
{name: "Jesse Welles"} or{year: 2024} |
Visually, this might look like:
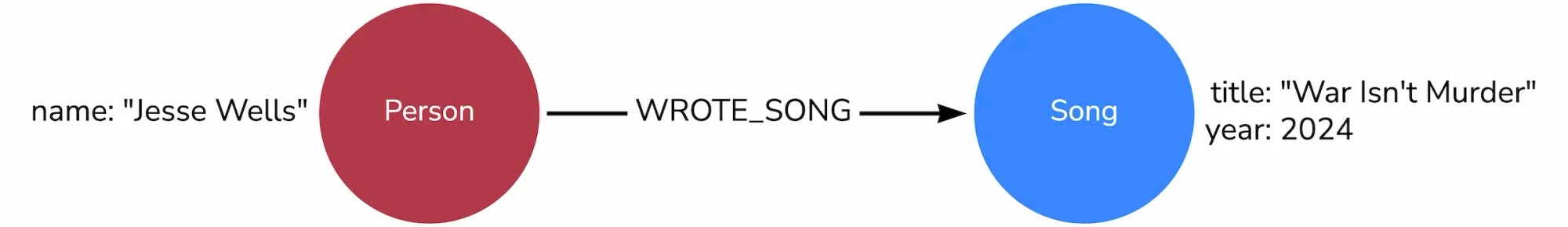
In Neo4j, data is the network. You don't just store data: you store connections.
Why Graph Databases Matter (Especially for the Humanities)
Most human stories are networks:
- Artists collaborate with others.
- Songs express ideas and emotions.
- Ideas influence people and travel through culture.
These relationships can't easily be captured in a simple table or spreadsheet.
Graph databases like Neo4j are ideal for this because they:
- Represent relationships directly. Connections are first-class citizens, not afterthoughts.
- Scale complexity gracefully. You can add new nodes and links without redesigning your schema.
- Mirror how humans think. We naturally see the world as webs of relationships: families, influences, meanings.
- Support discovery. Graphs make it easy to explore new patterns and connections visually.
In short, Neo4j lets us model culture in a way that feels natural to the humanities.
Neo4j's Ecosystem: Aura, Desktop, and Beyond
Neo4j offers several ways to use its database technology:
| Version | Description | Who It's For | Install Required? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neo4j Aura | Cloud-based, runs in your browser. Free tier option. |
Beginners, educators, small projects. |
❌ No |
| Neo4j Desktop | Local software for advanced users. |
Developers, researchers needing large data. |
✅ Yes |
| Neo4j Server / Enterprise |
Scalable, enterprise- level deployment. |
Organizations, production systems. |
✅ Yes |
This is, of course, an oversimplification, and Aura is offered as an enterprise solution with some enormous projects using it.
For this course, we'll use Neo4j Aura (free tier), because it's fast, safe, and works entirely in the browser. You'll create a free database in the cloud: no downloads, no configuration, no risk of "breaking" anything on your computer.
Neo4j in the Wellespring Context
The Wellespring Project uses Neo4j to organize and visualize the creative and cultural networks surrounding Jesse Welles. A small part of that model might look like this:
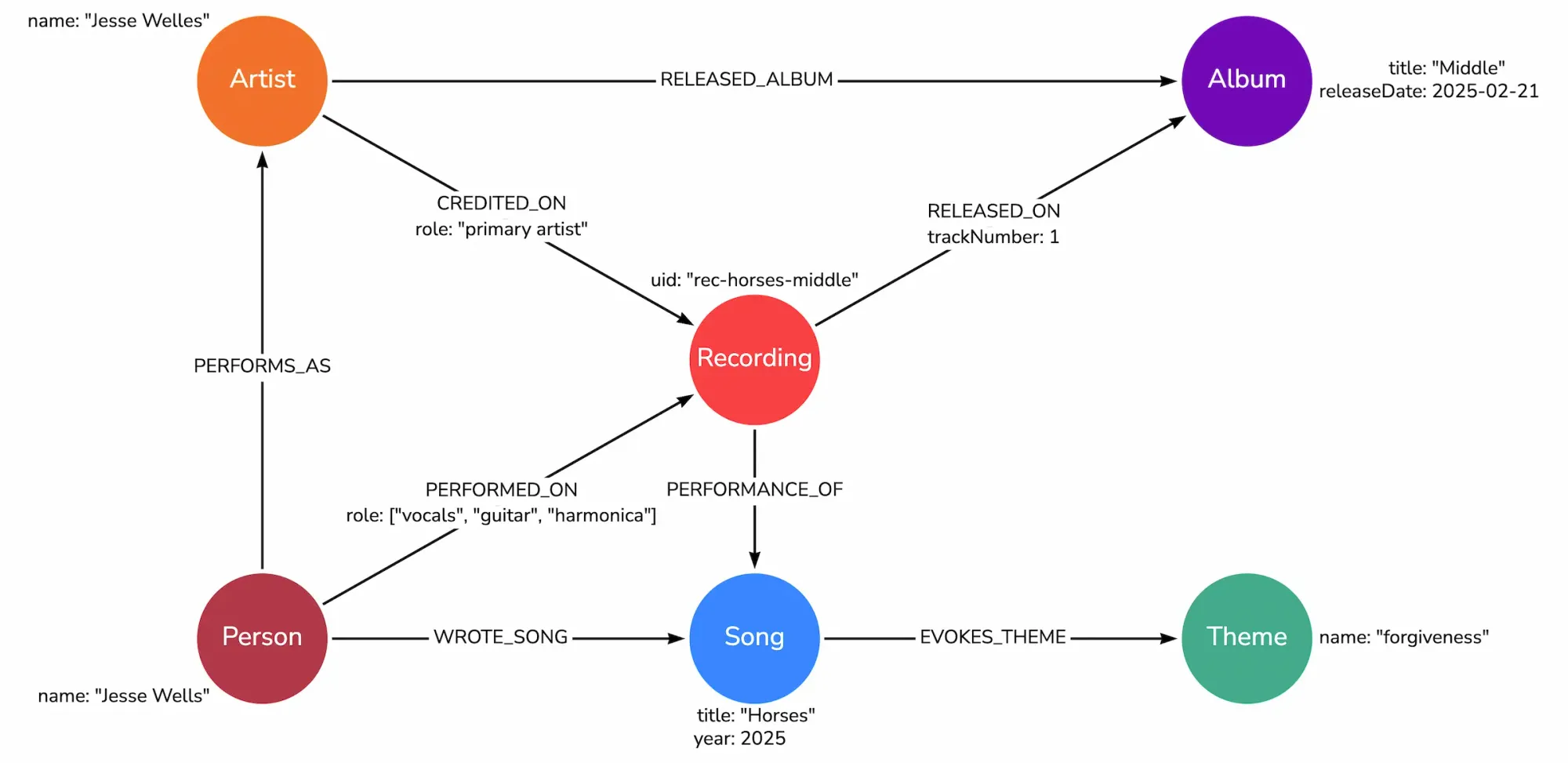
With Neo4j, you can:
- See how songs connect to people, themes, and places.
- Explore networks of influence and collaboration.
- Ask questions like:
- "Which songs share the same emotional theme?"
- "Who performed at the same events as Jesse Welles?"
- "What themes recur across his albums?"
This is how Neo4j turns human meaning into visual, searchable structure. While our project is using it for an analysis of Jesse Welles, his music, and cultural impact, you can use it for any domain in which you want to record, discover, and analyze meaningful connections; every area of the humanities—and so many other areas—could be explored using similar principles.
How Neo4j Differs from Relational Databases
| Feature | Relational (Tables) | Graph (Neo4j) |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Rows and columns | Nodes and relationships |
| Schema | Fixed and rigid | Flexible and adaptive |
| Relationships | Represented indirectly via "joins" | Represented directly as links |
| Best For | Accounting, inventory, transactions | Networks, connections, cultural data |
You don't need to master this comparison, but it's helpful to understand why Neo4j looks and feels different from other database systems that you might be familiar with.
Key Takeaways
- Neo4j is a graph database that represents information as connected nodes and relationships.
- It uses the property graph model (nodes, relationships, properties).
- Neo4j Aura (free tier) is ideal for beginners. No installation needed.
- Graphs model human meaning beautifully because they mirror the structure of relationships in culture, language, and art.
Knowledge Check & Reflection
Suggested Readings & Resources
- What is Neo4j? Getting Started with Neo4j.
- What is a Graph Database? Getting Started with Neo4j.
- Neo4j Documentation website
- Merki Sasaki, Bryce, and Joy Chao. Graph Databases for Beginners. Neo4j, 2021.
- Robinson, Ian, Jim Webber, and Emil Eifrem. Graph Databases: New Opportunities for Connected Data. Second edition. O’Reilly Media, 2015.